射线交叉法判断点是否位于几何体内部
射线交叉法可以用来计算一点是否在几何体内部,在本文中用于初始化有符号距离场的符号。其思路是,从网格内每一个点开始,沿x轴正向(沿任意一个方向均可)发出一条射线,判断这条射线穿过几何表面的次数,奇数次为内部点,偶数次为外部点。
下面先贴出来计算用到的概念和公式。
叉积/向量积/外积
三维空间中两个向量的叉积:
$$\textbf{u} \times \textbf{v} = |\textbf{u}||\textbf{v}|\sin\theta\textbf{n}$$矩阵表示:
$$\textbf{u} \times \textbf{v} = \begin{bmatrix} \textbf{i} & \textbf{j} & \textbf{k} \\ u_1 & u_2 & u_3 \\ v_1 & v_2 & v_3 \end{bmatrix} $$几何意义:叉积的结果是一个向量,模长等于两个向量为边所构成的平行四边形的面积,方向与两向量垂直,由右手定则决定。
有向面积
平面中\(\Delta{ABC}\),其中点\(A(x_A, y_A)\),\(B(x_B, y_B)\),\(C(x_C, y_C)\)。三角形的有向面积计算公式:
$$S_\Delta = \frac{1}{2} \begin{vmatrix} x_A & y_A & 1 \\ x_B & y_B & 1 \\ x_C & y_C & 1 \end{vmatrix} $$若A、B、C是逆时针方向排列,则三角形的有向面积是正的,顺时针为负,三点共线则为零。
应用:判断点D是否在\(\Delta{ABC}\)内部。
方法1(符号法):连接DA、DB、DC,若\(\Delta{DAB}\)、\(\Delta{DBC}\)、\(\Delta{DCA}\)的有向面积与\(\Delta{ABC}\)的有向面积符号相同,则点D在\(\Delta{ABC}\)内部。
方法2(面积法):当D在三角形ABC内部或边界上时,当且仅当\(S_{\Delta{ABC}}=S_{\Delta{DAB}}+S_{\Delta{DBC}}+S_{\Delta{DCA}}\)
三角形内一点的重心坐标
在三角形ABC中,对于三角形内任意一点P,存在一组实数\((\lambda_A,\lambda_B,\lambda_C)\)满足\(\lambda_A+\lambda_B+\lambda_C=1\),并且点P的位置可以通过如下关系定义:
$$\overrightarrow{OP}=\lambda_A\overrightarrow{OA}+\lambda_B\overrightarrow{OB}+\lambda_C\overrightarrow{OC}$$其中O是平面内任选的参考点,通常选三角形某个顶点以便于计算。这组实数\((\lambda_A,\lambda_B,\lambda_C)\)就是P点关于三角形ABC的重心坐标。
重心坐标与面积比之间的关系:P点关于三角形ABC的重心坐标中每个分量之比,等于P所在三个小三角形与该大三角形的面积之比:
$$S_{\Delta{PBC}}:S_{\Delta{PCA}}:S_{\Delta{PAB}}=\lambda_A:\lambda_B:\lambda_C$$代码实现
- 输入一点p,以及一个封闭STL实体,以及一个包围盒内的网格节点。对每一个节点:
- 遍历每一个三角面片,对每一个面片:
- 在x轴方向正投影平面上,判断点P是否在三角形内部。如果否,标记该节点为外部点并返回。
- 如果是内部,就计算它的重心坐标分量比(面积比),此时我们已知了交点的y,z坐标,需要进一步求出交点x坐标。
- 用重心坐标定义,求出交点的x坐标。
- 判断P的x坐标与交点x坐标的大小,可知道该点位于面片前方还是后方,只对前一种情况统计穿过次数。
- 统计穿过次数,如果为偶数,则标记该节点在几何体外部;奇数为内部。
- 符号场初始化完成。
每一个节点的判断逻辑是独立的,很容易用GPU并行实现。
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
#include "../define.h"
#include "../stl.h"
// 计算三角形 O(0, 0) A(x1, y1) B(x2, y2) 的有向面积, OAB逆时针排列时是正
int orientation(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float& twice_signed_area) {
twice_signed_area = x1 * y2 - x2 * y1;
if (twice_signed_area > 0) return 1;
else if (twice_signed_area < 0) return -1;
// twice_signed_area 为0, 有可能是OAB共线(或AB重合), 此时点可能在边AB上, 此时根据AB的关系返回其符号
// 区分以下几种情况, 是为了避免点位于两相邻三角形的共向边上时重复计数
else if(y1 > y2) return 1;
else if(y1 < y2) return -1;
else if(x1 < x2) return 1;
else if(x1 > x2) return -1;
else return 0; // 此时OAB三点有任意两点重合, 直接认为在三角形外
}
// 判断平面上一点P(x0, y0)是否在三角形ABC内部, 其中 A(x1, y1), B(x2, y2), C(x3, y3)
// 如果在内部, 顺便计算其重心坐标(lambda_a, lambda_b, lambda_c), 其中 lambda_a + lambda_b + lambda_c = 1
// 重心坐标与面积存在关系 lambda_a : lambda_b : lambda_c = Spbc : Spca : Spab
bool point_in_triangle_2d(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float x3, float y3, float& lambda_a, float& lambda_b, float& lambda_c) {
// 将坐标原点移到x0, y0, 简化处理
x1 -= x0; x2 -= x0; x3 -= x0;
y1 -= y0; y2 -= y0; y3 -= y0;
int sign1 = orientation(x2, y2, x3, y3, lambda_a); // 三角形PBC 的有向面积*2
if (sign1 == 0) return false; // 此时面片与x轴平行, 认为不相交
int sign2 = orientation(x3, y3, x1, y1, lambda_b); // 三角形PCA
if (sign2 != sign1) return false; // 符号不同, 在三角形外部
int sign3 = orientation(x1, y1, x2, y2, lambda_c); // 三角形PAB
if (sign3 != sign1) return false; // 符号不同, 在三角形外部
// 面积比归一化为重心坐标
float sum = lambda_a + lambda_b + lambda_c;
lambda_a /= sum;
lambda_b /= sum;
lambda_c /= sum;
return true;
}
// 从p点出发, 沿x正向发出射线, 判断是否与三角面片相交, 如果相交则计算其交点位置
bool ray_casting(const Vertice& p, const Triangle& tri, Vertice& intersection) {
float lambda_a, lambda_b, lambda_c;
// 判断点与三角形在x方向的正投影有没有相交
if (point_in_triangle_2d(p.y, p.z,
tri.vertices[0].y, tri.vertices[0].z,
tri.vertices[1].y, tri.vertices[1].z,
tri.vertices[2].y, tri.vertices[2].z,
lambda_a, lambda_b, lambda_c)) {
intersection.x = lambda_a * tri.vertices[0].x + lambda_b * tri.vertices[1].x + lambda_c * tri.vertices[2].x;
intersection.y = lambda_a * tri.vertices[0].y + lambda_b * tri.vertices[1].y + lambda_c * tri.vertices[2].y;
intersection.z = lambda_a * tri.vertices[0].z + lambda_b * tri.vertices[1].z + lambda_c * tri.vertices[2].z;
return intersection.x > p.x; // 射线沿x轴正方向行走, 面片如果在p的左侧, 则不算穿过
}
return false;
}
TEST(SDFTest, test_ray_casting) {
std::vector<::Triangle> triangles;
Vertice min_bound, max_bound;
STL::read_binary_stl("../data/grain_bin.stl", triangles, min_bound, max_bound);
EXPECT_EQ(triangles.size(), 780);
Vertice p((max_bound - min_bound)*0.3);
printf("p (%f, %f, %f)\n", p.x, p.y, p.z);
uint count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < triangles.size(); i++) {
Vertice intersection;
if (ray_casting(p, triangles[i], intersection)) {
printf("\nintersection %d:\n", count);
printf("\tintersection (%f, %f, %f)\n", intersection.x, intersection.y, intersection.z);
printf("\ttriangle A(%f, %f, %f) B(%f, %f, %f) C(%f, %f, %f)\n\n",
triangles[i].vertices[0].x, triangles[i].vertices[0].y, triangles[i].vertices[0].z,
triangles[i].vertices[1].x, triangles[i].vertices[1].y, triangles[i].vertices[1].z,
triangles[i].vertices[2].x, triangles[i].vertices[2].y, triangles[i].vertices[2].z
);
count++;
}
}
printf("count=%d\n", count);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);
return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}
一个关键问题,刚好落在三角形边上或顶点上的点算不算穿过面片?
以上代码实现中,落在三角形边上或顶点上的点O,返回的三角形OAB的有向面积等于0,但仍需要对不同情况进行区分。
当三角形OAB有向面积为零时,有可能
- 三角形其中两点重合(别忘了它是空间三角形在x方向的正投影)。此时要么射线刚好穿过顶点,要么面片与射线平行。
- 三个点共线,分两种情况,AB指向正方向或负方向,此时AB的方向来决定其符号。
以下这段逻辑来处理有向面积为零时的不同情况:
int orientation(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float& twice_signed_area) {
twice_signed_area = x1 * y2 - x2 * y1;
if (twice_signed_area > 0) return 1;
else if (twice_signed_area < 0) return -1;
else if(y1 > y2) return 1;
else if(y1 < y2) return -1;
else if(x1 < x2) return 1;
else if(x1 > x2) return -1;
else return 0;
}
对于射线落在共享边的情形,该处理可以保证只被计数一次。如下图,P点与(有向)边AB组成的三角形PAB有向面积为正0,而与边BA组成三角形PBA的有向面积为负0,最终判定P与三角形ABC相交,与三角形ADB不相交。
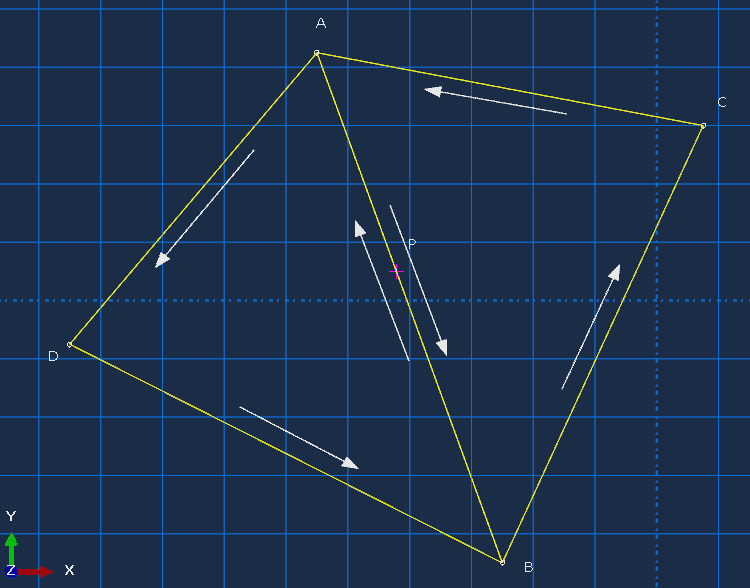
测试代码:
// 射线交点在共享边
TEST(SDFTest, test_point_in_triangle_2d) {
// p (0, 0)
// A (-1, 5)
// B (1, -5)
// C (5, 3)
// D (-6, -2)
float a, b, c;
// P是否在ABC内部
bool b1 = point_in_triangle_2d(0.0f, 0.0f,
-1.0f, 5.0f,
1.0f, -5.0f,
5.0f, 3.0f,
a, b, c
);
// P是否在ADB内部
bool b2 = point_in_triangle_2d(0.0f, 0.0f,
-1.0f, 5.0f,
-6.0f, -2.0f,
1.0f, -5.0f,
a, b, c
);
ASSERT_TRUE(b1);
ASSERT_FALSE(b2);
}
对于射线落在共享顶点的情况,计数也是正确的,如下情形,只会对三角形AED判定穿过。
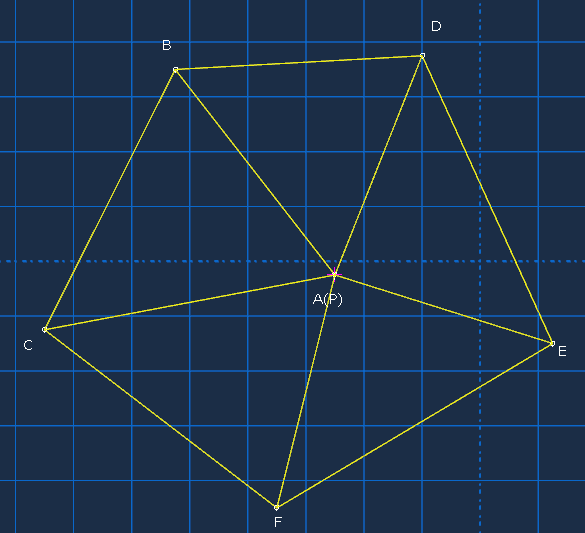
测试代码:
// 射线交点在共享顶点
TEST(SDFTest, test_point_in_triangle_2d_2) {
// p (0, 0)
// A (0, 0)
// B (-3, 5)
// C (-5, -2)
// D (3, 6)
// E (4, -3)
// F (-1, -6)
Vertice p(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
Vertice A(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f);
Vertice B(-3.0f, 5.0f, 0.0f);
Vertice C(-5.0f, -2.0f, 0.0f);
Vertice D(3.0f, 6.0f, 0.0f);
Vertice E(4.0f, -3.0f, 0.0f);
Vertice F(-1.0f, -6.0f, 0.0f);
float a, b, c;
std::vector<std::vector<Vertice>> test_case = {{p, A, B, C}, {p, A, C, F}, {p, A, F, E}, {p, A, E, D}, {p, A, D, B}};
std::vector<bool> result;
std::vector<bool> assertion = { false, false, false, true, false };
for (const auto& v : test_case) {
bool ret = point_in_triangle_2d(v[0].x, v[0].y,
v[1].x, v[1].y,
v[2].x, v[2].y,
v[3].x, v[3].y,
a, b, c
);
result.push_back(ret);
}
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
ASSERT_EQ(result[i], assertion[i]);
}
}
这个算法来自: mesh2sdf - https://github.com/wang-ps/mesh2sdf/blob/master/csrc/makelevelset3.cpp
2025.04.13 补充:实测上面的代码有几率会错判(内点判为外,外点判为内)。原因是float的精度问题,大部分情况下不会出现0面积,所以需要做一个修正:
__device__ int orientation(float x1, float y1, float x2, float y2, float& twice_signed_area) {
twice_signed_area = x1 * y2 - x2 * y1;
// if (twice_signed_area != 0.0f && abs(twice_signed_area - 0) < FLOAT_TOLERANCE) printf("float error!!\n");
if (abs(twice_signed_area - 0) < FLOAT_TOLERANCE) { // 小于一定容差的都算为0, 避免误判
if(y1 > y2) return 1;
else if(y1 < y2) return -1;
else if(x1 < x2) return 1;
else if(x1 > x2) return -1;
else return 0;
} else {
if (twice_signed_area > 0) return 1;
else return -1;
}
}
这个代码运行得很好。
测试代码:
//
// Created by wangh on 2025/4/13.
//
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "../define.h"
#include "../stl.h"
Grid field_grid;
std::vector<float> field;
std::vector<Triangle> triangles_cube;
std::vector<Vertice> vertices;
float *d_field;
Grid *d_grid;
Triangle *d_triangles_cube;
void create_cube() {
// 正方体8个顶点
vertices = {
{0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f},
{1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f},
{1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f},
{0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f},
{0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f},
{1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f},
{1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f},
{0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f}
};
// 向x,y,z轴三个方向平移1
// Vertice v1 = {1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f};
// for (Vertice& vertice : vertices) {
// vertice = vertice + v1;
// }
triangles_cube = {{vertices[1 - 1], vertices[2 - 1], vertices[3 - 1]},
{vertices[1 - 1], vertices[3 - 1], vertices[4 - 1]},
{vertices[4 - 1], vertices[3 - 1], vertices[7 - 1]},
{vertices[4 - 1], vertices[7 - 1], vertices[8 - 1]},
{vertices[8 - 1], vertices[7 - 1], vertices[6 - 1]},
{vertices[8 - 1], vertices[6 - 1], vertices[5 - 1]},
{vertices[5 - 1], vertices[6 - 1], vertices[2 - 1]},
{vertices[5 - 1], vertices[2 - 1], vertices[1 - 1]},
{vertices[2 - 1], vertices[6 - 1], vertices[7 - 1]},
{vertices[2 - 1], vertices[7 - 1], vertices[3 - 1]},
{vertices[5 - 1], vertices[1 - 1], vertices[4 - 1]},
{vertices[5 - 1], vertices[4 - 1], vertices[8 - 1]},
};
STL::write_ascii_stl("./cube.stl", triangles_cube);
}
void init_cuda_memory() {
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_field, field.size() * sizeof(float));
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_triangles_cube, triangles_cube.size() * sizeof(Triangle));
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_grid, sizeof(Grid));
cudaMemcpy(d_field, field.data(), field.size() * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_triangles_cube, triangles_cube.data(), triangles_cube.size() * sizeof(Triangle), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_grid, &field_grid, sizeof(Grid), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
}
TEST(SIGNED_FIELD_TEST, test_cube) {
field_grid.grid_size = {8, 8, 8};
field_grid.min_bound = { -0.05f, -0.05f, -0.05f };
field_grid.grid_step = { 0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f };
field_grid.num_grid_points = field_grid.grid_size.x * field_grid.grid_size.y * field_grid.grid_size.z;
field.resize(field_grid.num_grid_points, FLT_MAX);
create_cube();
init_cuda_memory();
init_signed_field(d_field, d_grid, d_triangles_cube, triangles_cube.size(), field_grid.num_grid_points, field);
cudaMemcpy(field.data(), d_field, field.size() * sizeof(float), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
uint count = 0;
for (uint i = 0; i < field.size(); i++) {
if (field[i] > 0) {
count++;
}
float3 coord = field_grid.coordinate(i);
if (coord.x > 0.0f && coord.x < 1.0f && coord.y > 0.0f && coord.y < 1.0f && coord.z > 0.0f && coord.z < 1.0f) {
if (field[i] < 0) { // 内点误判成外点
uint3 ijk = field_grid.index_3d(i);
printf("error1 ijk: %d, %d, %d\n", ijk.x, ijk.y, ijk.z);
}
ASSERT_TRUE(field[i] >= 0);
} else {
if (field[i] >= 0) { // 外点误判成内点
uint3 ijk = field_grid.index_3d(i);
printf("error2 ijk: %d, %d, %d\n", ijk.x, ijk.y, ijk.z);
}
ASSERT_TRUE(field[i] < 0);
}
}
printf("count: %d\n", count);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);
return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
}